Let's have a look at what verb moods are so that we can use them correctly and avoid mixing the moods within the same sentence.
What Are Verb Moods Exactly?
Verb moods express a tone or attitude in the sentence. They are not a tense.
There are five verb moods in English:
- indicative
- imperative
- interrogative
- conditional
- subjunctive
Let's taker a closer look at each mood.
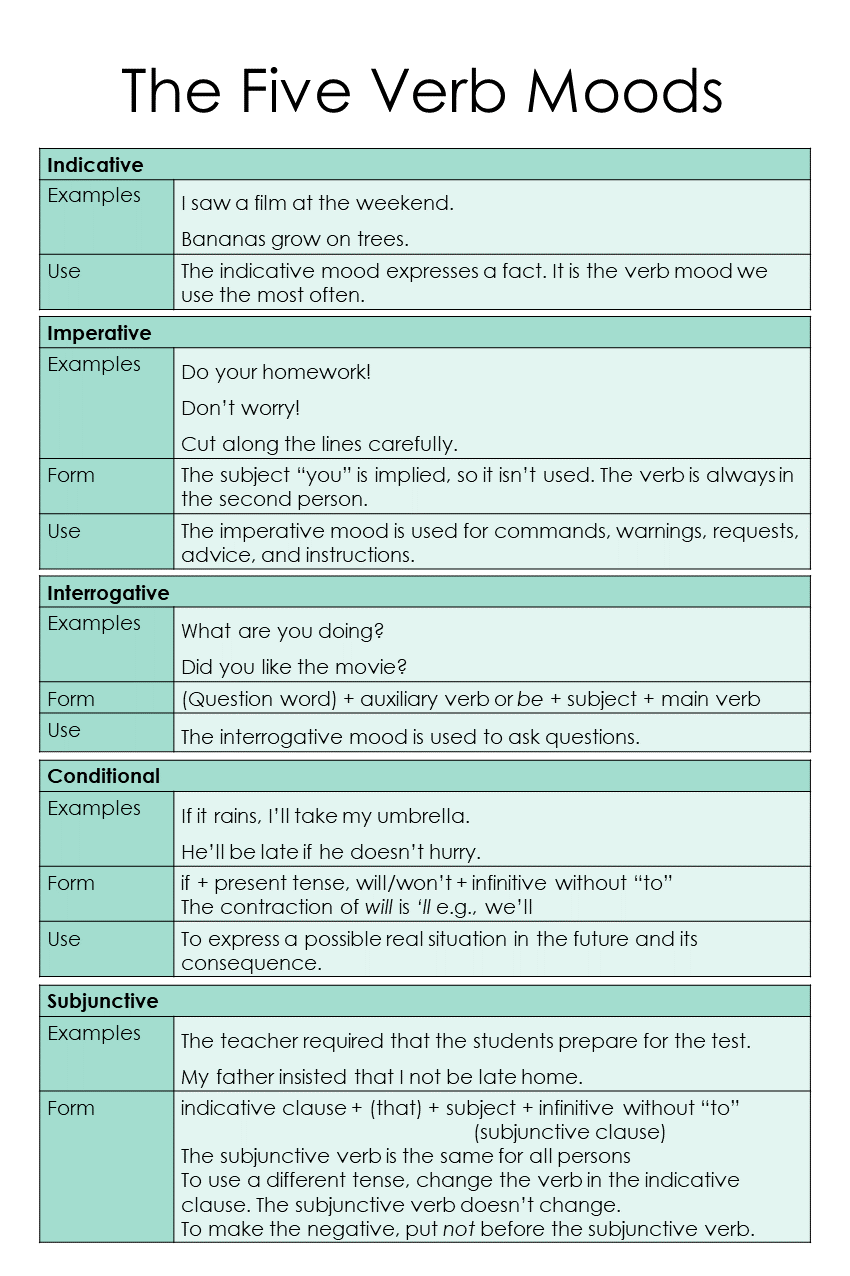
Indicative Mood
The indicative mood expresses a fact. It is the verb mood we use the most often.
Examples:
I saw a film at the weekend.
Bananas grow on trees.
Imperative Mood
The imperative mood is used for commands, warnings, requests, advice, and instructions.
Forming the imperative mood:
The subject “you” is implied, so it isn’t used. The verb is always in the second person.
Examples:
Do your homework!
Don’t worry!
Cut along the lines carefully.
Interrogative Mood
The interrogative mood is used to ask questions.
Forming the interrogative mood:
(Question word) + auxiliary verb or be + subject + main verb
Examples:
What are you doing?
Did you like the movie?
Conditional Mood
The conditional mood expresses a statement that depends on something happening. There is an if- clause (the dependent clause), which states the condition, and a consequence clause (the main clause).
There are four conditional moods:
- zero conditional
- first conditional
- second conditional
- third conditional
There is also the “mixed conditional” which uses a combination of the above conditionals.
Examples:
If it rains, I’ll take my umbrella. (first conditional - a possible real situation in the future and its consequence)
He would be happy if he won the competition. (second conditional - an imaginary or hypothetical situation in the present or future, and its consequence)
Subjunctive Mood
The subjunctive mood expresses a wish, demand, suggestion, or hypothetical (imaginary) situation.
It states something that is contrary to fact, which means that the situation or condition is not a reality.
The subjunctive follows certain verbs (and their noun form) and adjectives.
It is used in the second conditional
It is used after the phrases if, as if, suppose, and wish.
It is used in formal language more than informal language. In spoken language people may use an indicative form instead of the subjunctive. This has become more common over time, so it isn’t considered incorrect. However, in writing students need to use the correct subjunctive form.
Examples:
It is imperative that the work be finished on time.
The teacher required that the students prepare for the test.
If I were you, I would use blue for the background.
I wish I were better at drawing.
Practice Worksheets
If you're after worksheets suitable for Grade 8, to practice the five verb moods, you can find those here.
If you'd like a board game that will get your students more confident with verb moods, then you can find that here.
Here's a summary of everything we've covered with verb moods.
If you've covered verb moods with your students, then you may be ready to look at shifts in mood. You can find worksheets here.




Comments ()